Codice di guasto del climatizzatore di casa Midea, fasi di riparazione e link al codice di guasto del climatizzatore centrale
In primo luogo, i modelli di condizionatori domestici precedenti al 2019
(A) E. M. H. G serie DC inverter appendini.
E0 Indicazione errore parametro EEPROM
E1 La comunicazione tra l'unità interna e l'unità esterna è difettosa Il rilevamento dell'attraversamento dello zero E2 fallisce
E3 Velocità della ventola fuori controllo
E4 Protezione del fusibile di temperatura scollegato Il sensore di temperatura esterna E5 è guasto Il sensore di temperatura interna E6 è guasto P0 Protezione del modulo
P1 Protezione da sovratensione o sottotensione P2 Protezione della temperatura massima del compressore
P4 Protezione posizione compressore inverter DC
(2) Convertitore di frequenza CC a colonna N, W appeso alla macchina.
E0 Indicazione errore parametro EEPROM
La comunicazione E1 tra l'unità interna e l'unità esterna è difettosa Il rilevamento del passaggio a zero E2 non funziona
E3 Velocità della ventola fuori controllo
E4 Protezione del fusibile di temperatura scollegato
Il sensore di temperatura esterna E5 è difettoso o la 807EEPROM esterna è difettosa Il sensore di temperatura interna E6 è difettoso
P0 Protezione del modulo
P1 Protezione da sovratensione o sottotensione P2 Protezione della temperatura massima del compressore
P4 Protezione posizione compressore inverter DC
(3) Macchina pensile a conversione di frequenza CC completa a colonna C.
E1 Indicazione errore parametro EEPROM
E2 La comunicazione tra l'unità interna e l'unità esterna è difettosa E3 Errore di attraversamento dello zero
E4 velocità del ventilatore fuori controllo
Il sensore di temperatura esterna E5 è difettoso o il parametro E-square esterno è difettoso Il sensore di temperatura interna E6 è difettoso
La velocità del ventilatore esterno E7 è fuori controllo
La comunicazione sulla scheda display E8 è difettosa
Il modulo IPM E9 è guasto P0 Protezione modulo
P1 Protezione da sovratensione o sottotensione P2 Protezione della temperatura massima del compressore
P3 Protezione contro le basse temperature esterne
P4 Protezione posizione compressore inverter DC
(4) Blocco della conversione di frequenza CC della colonna I.
E0 Indicazione errore parametro EEPROM
E1 La comunicazione tra l'unità interna e l'unità esterna è difettosa Il rilevamento dell'attraversamento dello zero E2 fallisce
E3 Velocità della ventola fuori controllo
E5 Il sensore di temperatura esterna è difettoso o il parametro E square esterno è difettoso Il sensore di temperatura interna E6 è difettoso
La velocità del ventilatore esterno E7 è fuori controllo E8 La rimozione della polvere è difettosa
P0 Protezione del modulo
P1 Protezione da sovratensione o sottotensione P2 Protezione della temperatura massima del compressore
P3 Protezione contro le basse temperature esterne
P4 Protezione posizione compressore inverter DC
(5) Appendici per inverter CC serie solare J, K, L, R, K
E0 Indicazione errore parametro EEPROM
E1 La comunicazione tra l'unità interna e l'unità esterna è difettosa Il rilevamento dell'attraversamento dello zero E2 fallisce
E3 Velocità della ventola fuori controllo
E5 Il sensore di temperatura esterna è difettoso o il parametro E square esterno è difettoso Il sensore di temperatura interna E6 è difettoso
La velocità del ventilatore esterno E7 è fuori controllo E8 Conflitto di modalità
Protezione modulo P0
P1 Protezione da sovratensione o sottotensione P2 Protezione della temperatura massima del compressore
P3 Protezione contro la bassa temperatura esterna P4 Protezione della posizione del compressore dell'inverter DC
(6) 50FBPY, 50BPY macchina armadio di conversione di frequenza
E01 Protezione del modulo quattro volte all'ora
Protezione della temperatura di scarico per E03 tre volte all'ora
Il pannello interno P01 non può essere protetto dal pannello esterno per 2 minuti P02 Protezione modulo IPM
P03 Protezione da alta e bassa tensione
P04 Apertura o cortocircuito del sensore di temperatura interna (ambiente, temperatura)
P05 Apertura o cortocircuito del sensore di temperatura esterna (temperatura alta o bassa)
P06 Protezione temperatura evaporatore interno spegnimento compressore (alta temperatura o bassa temperatura) P07 Protezione alta temperatura condensatore esterno spegnimento del compressore
P09 La temperatura di scarico esterna è troppo alta per spegnere il compressore P10 Protezione della temperatura massima del compressore
P11 Sbrinamento o protezione aria fredda
La ventola interna di un P12 è surriscaldata
P13 Il ventilatore interno non comunica con il quadro elettrico per tre minuti.
(7) Condizionatore incorporato con uscita laterale dell'aria della serie Midea
Errore nella lettura del parametro EEPROM quando E0 è acceso
E1 Il sensore T1 della temperatura ambiente interna è aperto o in cortocircuito E2 Il sensore T2 della temperatura dell'evaporatore interno è aperto o in cortocircuito E3 Il sensore T3 della temperatura del condensatore è aperto o in cortocircuito. Temperatura del condensatore T3 sensore aperto o in cortocircuito
Protezione quadrupla corrente Pd
(VIII) A, B, FA, FB, FC, GA, GC, H, HA, HB, J, K, N, P, Q1, Q2, Q3, U, V, V1, W, X e altre serie
spaccatura macchine
Errore nella lettura del parametro EEPROM quando E1 è alimentato Errore nel rilevamento dell'attraversamento dello zero di E2
E3 Velocità della ventola fuori controllo
E4 Protezione da quattro correnti
E5 Sensore di temperatura interna aperto o in cortocircuito
E6 Il sensore di temperatura dell'evaporatore interno è aperto o in cortocircuito E8 Guasto al reset del filtro
(IX) Serie Q.
E1 Il sensore T1 è guasto E2 Il sensore T2 è guasto E3 Il sensore T3 è guasto
Il sensore E4 T4 è difettoso
La comunicazione di rete E5 è difettosa E6 Protezione esterna
L'umidificatore E7 è difettoso
E8 Mancata rimozione della polvere silenziosa E9 Errore EEPROM
(10) GA, armadio serie K, J, N, P, Q1, Q2, Q3, armadio serie R, S1, S2, S3, S6, U (U1), V, W, V2 e altre serie
Il sensore E1 T1 è difettoso Il sensore E2 T2 è difettoso
E3 Il sensore T3/T4 è difettoso
E4 T4 Guasto del sensore (inverter)
E5 guasto della comunicazione di rete E6 guasto esterno
L'umidificatore E7 è difettoso
E8 La rimozione elettrostatica della polvere è difettosa
EQ La porta automatica è difettosa
Secondo. casa aria condizionamento 2019 e oltre.
(1) Il interno unità display bordo può mostra il guasto 1, visualizzazione guasto macchina armadio.
| codice protetto | Esprimere il contenuto | codice protetto | Esprimere il contenuto |
| OP | Malfunzionamento del modulo PM | E0 | Malfunzionamento del parametro EEPROM |
| P1 | Protezione di tensione | E1 | Malfunzionamento del sensore T1 |
| P2 | Protezione della temperatura massima del compressore | E2 | Malfunzionamento del sensore T2 |
| P4 | Protezione evaporatore interno arresto compressore (alta o bassa temperatura) | E3 | T3/T4, malfunzionamento del sensore di scarico o malfunzionamento del parametro lato E dell'unità esterna |
| P5 | Protezione dalle alte temperature per il condensatore esterno e spegnimento del compressore | E5 | Guasto di comunicazione tra la scheda di controllo principale e la scheda dei tasti del display |
| P6 | Protezione della posizione del compressore a frequenza variabile DC | E8 | Guasto della comunicazione interna ed esterna |
| P7 | Spegnere il compressore quando la temperatura di scarico esterna è troppo alta. | E9 | Malfunzionamento dell'apertura e della chiusura della porta |
| P8 | Conflitto di modelli | Eb | Guasto di stallo del ventilatore CC interno |
| P9 | Ventola di spegnimento dell'aria fredda | L0 | Limite di frequenza alta e bassa temperatura dell'evaporatore |
| PA | Protezione della griglia | L1 | Limite di frequenza dell'alta temperatura del condensatore |
| Pd | protezione dalla corrente | L2 | Limite di frequenza della temperatura di scarico del compressore |
| L3 | Limite di frequenza della corrente |
2, appendere su difetto display.
E0 Guasto parametro EEPROM
E1 La comunicazione tra l'unità interna e l'unità esterna è difettosa E2 Lo zero crossing rileva il guasto
E3 Velocità del ventilatore interno fuori controllo
E5 Il sensore della temperatura esterna è guasto Il sensore della temperatura interna E6 è guasto E7 Guasto di stallo del ventilatore CC esterno
P0 Protezione modulo IPM
P1 Protezione da sovratensione o sottotensione
P2 Protezione della temperatura superiore del compressore P4 Protezione della posizione del compressore con inverter DC
(2) La scheda di manutenzione della conversione di frequenza è in grado di visualizzare il guasto.
| codice protetto | Esprimere il contenuto | codice protetto | Esprimere il contenuto |
| P0 | Protezione del modulo dell'unità esterna | E0 | Guasto dei parametri EEPROM dell'unità interna |
| P1 | Protezione di tensione | E1 | Guasto della comunicazione interna ed esterna |
| P10 | Protezione dalla bassa tensione | E2 | Guasto di rilevamento dell'attraversamento dello zero dell'unità interna |
| P11 | Protezione dall'alta tensione | E3 | Guasto di stallo del ventilatore dell'unità interna |
| P12 | Malfunzionamento del 341MCE | E5 | Sensore di temperatura dell'unità esterna o guasto del lato E |
| P2 | Protezione della temperatura massima del compressore | E50 | Sensore di temperatura dell'unità esterna |
| P4 | Protezione di retroazione per il compressore dell'unità esterna | E51 | Guasto dell'unità esterna E |
| P40 | Errore di comunicazione tra il chip di controllo principale e il chip driver | E52 | Malfunzionamento del sensore di temperatura T3 della batteria esterna |
| P41 | Guasto al circuito di campionamento della corrente del compressore | E53 | Ambiente esterno Malfunzionamento del sensore di temperatura T4 |
| P42 | Guasto all'avvio del compressore | E54 | Malfunzionamento del sensore della temperatura di scarico esterna |
| P43 | Protezione dalla perdita di fase del compressore | E55 | Malfunzionamento del sensore della temperatura di ritorno dell'aria esterna |
| P44 | Protezione del compressore a velocità zero | E6 | Malfunzionamento del sensore di temperatura della pesca interna |
| codice protetto | Esprimere il contenuto | codice protetto | Esprimere il contenuto |
| P45 | Anomalia di sincronizzazione 341PWM | E60 | Malfunzionamento del sensore di temperatura T1 dell'unità interna |
| P46 | Protezione dallo stallo del compressore | E61 | Malfunzionamento del sensore di temperatura T2 dell'unità interna |
| P47 | Compressore IPDU bloccato | E7 | Guasto di stallo del ventilatore CC dell'unità esterna |
| P48 | Regolazione di spegnimento del compressore IPDU | Eb | Guasto di comunicazione tra il pannello interno e il pannello del display |
| P49 | Guasto di sovracorrente del compressore | ||
| P6 | Protezione dello scarico del compressore dalle alte temperature | P9 | Protezione dell'evaporatore dalle alte e basse temperature |
| P8 | protezione dalla corrente | P90 | Protezione dell'evaporatore dalle alte temperature |
| P80 | Protezione della corrente dell'unità interna | P91 | Protezione dell'evaporatore dalle basse temperature |
| P81 | Protezione dalla corrente dell'unità esterna | PA | Protezione ad alta temperatura per il condensatore |
| P82 | Guasto al circuito di campionamento della corrente alternata in ingresso | PF | Avvio PFC arresto della risata |
| codice protetto | Esprimere il contenuto |
| L0 | Limite di frequenza alta e bassa temperatura dell'evaporatore |
| L1 | Limite di frequenza dell'alta temperatura del condensatore |
| L2 | Limite di frequenza della temperatura di scarico del compressore |
| L3 | Limite di frequenza della corrente |
| L5 | Frequenza limitata dalla tensione |
| L6 | Limite di frequenza del guasto PFC |
Tre. il Uniti Stati casa frequenza conversione aria condizionamento manutenzione passi.
(a) Guasto del parametro E0 EEPROM: controllare la scheda di controllo elettrico interna o sostituire la scheda di controllo elettrico interna.
- Se il quadro visualizza il sensore di temperatura interna E1 anormale, il quadro visualizza il sensore di temperatura dell'evaporatore interno E2 anormale, e il riaggancio Se l'armadio visualizza il sensore di temperatura interna E1 anormale, l'armadio visualizza il sensore di temperatura dell'evaporatore interno E2 anormale e il blocco visualizza il sensore di temperatura interna E6 anormale, controllare la scheda di controllo elettrica interna e il sensore di temperatura; fasi di risoluzione dei problemi.
Fase 1: Controllare se il sensore di temperatura interna è collegato correttamente e se ci sono danni o rotture nel gruppo di fili intermedio tra il gruppo di fili del sensore e il collegamento alla scheda madre Fase 2: Sostituire con un buon sensore di temperatura (se non c'è un sensore pronto per l'uso, saltare questa fase e gruppo di fili del sensore e il collegamento alla scheda madre Fase 2: Sostituire con un buon sensore di temperatura (se non c'è un sensore già pronto, saltare questa fase e seguire direttamente il punto 3). seguire direttamente il passo 3). Se il fenomeno dell'ostacolo viene annullato, determinare il guasto del sensore e sostituirlo. Se il fenomeno dell'ostacolo non può essere annullato, determinare il guasto del sensore. Se il fenomeno dell'ostacolo non può essere annullato, determinare il guasto del controllo elettrico interno e sostituire il controllo elettrico interno.
Fase 3: Dopo aver verificato che il sensore sia collegato correttamente, scollegare la spina del sensore della temperatura ambiente interna per avvicinarne la temperatura a quella ambiente. Utilizzare un misuratore per misurare il valore di resistenza del sensore.
Fase 4: stimare approssimativamente la temperatura interna in questo momento e controllare il valore della resistenza corrispondente
sul termometro: (Nota: quando la temperatura ambiente è di 25 gradi, il valore della resistenza del sensore corrisponde a 10K. Con l'aumento della temperatura, il valore della resistenza del sensore diminuisce e con la diminuzione della temperatura, il valore della resistenza aumenta). Se il valore di resistenza della temperatura si discosta notevolmente (la deviazione del valore di resistenza della temperatura è superiore a 5 gradi, il valore di resistenza aumenta). Se il valore di resistenza della temperatura si discosta notevolmente (lo scostamento del valore di resistenza della temperatura è superiore a 5 gradi), il sensore è difettoso e il sensore di temperatura interna deve essere sostituito. Il sensore di temperatura interna deve essere sostituito.
Se la deviazione del valore di resistenza della temperatura è molto piccola (la deviazione del valore di resistenza della temperatura è inferiore a 5 gradi), il controllo elettrico è difettoso e il controllo elettrico interno deve essere sostituito. Se la deviazione del valore di resistenza della temperatura è molto piccola (la deviazione del valore di resistenza della temperatura è inferiore a 5 gradi), il controllo elettrico è difettoso e il controllo elettrico interno deve essere sostituito.
- Display del cabinet E3, display di blocco E5: guasto del sensore della temperatura esterna; controllare il controllo elettrico esterno, il sensore della temperatura esterna, Controllare il controllo elettrico esterno, il sensore di temperatura esterna, le fasi di risoluzione dei problemi.
Fase 1: collegare il tester di manutenzione della conversione di frequenza e osservare il guasto visualizzato sulla scheda piccola
Se viene visualizzato E51 (guasto EEPROM dell'unità esterna) Ostacolo: sostituire il comando elettrico esterno.
Fase 2: se il tester di manutenzione della conversione di frequenza visualizza un errore del sensore, bloccare la gamma in base al seguente codice.
E52 (guasto al sensore di temperatura della bobina esterna T3): verificare il valore della resistenza corrispondente del termometro.
E53 (guasto del sensore di temperatura dell'ambiente esterno T4): verificare il valore della resistenza corrispondente del termometro.
E54 (guasto al sensore della temperatura di scarico esterna): verificare il valore della resistenza corrispondente del termometro)
E55 (guasto al sensore della temperatura dell'aria esterna di ritorno): verificare il valore della resistenza corrispondente del termometro.
Fase 3: dopo aver bloccato l'intervallo di guasti, è possibile fare riferimento alle fasi di risoluzione dei problemi per i guasti E1 per la risoluzione dei problemi.
- Display del cabinet E5, scheda madre e scheda di pressione dei tasti del display non riescono a comunicare, controllare la scheda madre interna, la scheda di pressione dei tasti e il connettore.
Metodo 1: portare una scheda di visualizzazione del quadro a frequenza variabile normalmente funzionante, indipendentemente dal modello, e collegarla al controllo elettronico interno. Se il guasto scompare, determinare il guasto del controllo elettronico del display originale e sostituirlo; se il guasto non scompare, si determina un guasto del controllo elettrico interno e il controllo elettrico interno deve essere sostituito. Se il guasto scompare, determinare il guasto del controllo elettronico del display originale e sostituirlo; se il guasto non scompare, si determina un guasto del controllo elettrico interno e il controllo elettrico interno deve essere sostituito.
Metodo 2: Allo stesso modo, portare un normale controllo elettronico interno del quadro di conversione di frequenza, indipendentemente dal modello, collegare l'alimentazione e tutti i carichi e la scheda di visualizzazione. e tutti i carichi e la scheda di visualizzazione: se il guasto E5 scompare (nota: a causa di possibili problemi di compatibilità con il controllo elettronico interno, finché il guasto E5 non viene visualizzato, è possibile giudicarlo). finché il guasto E5 non viene visualizzato, può essere giudicato)
Se il guasto E5 non scompare, confermare il guasto del controllo elettronico del display e sostituire il controllo elettronico del display. Se il guasto E5 non scompare, confermare il guasto del controllo elettronico del display e sostituire il controllo elettronico del display.
Metodo 3: se non vi sono condizioni per la visualizzazione del controllo elettronico o del controllo elettronico interno, seguire i seguenti passaggi per il test.
Fase 1: Osservare se il gruppo di fili di collegamento del display è danneggiato. Se è danneggiato, è possibile sostituire direttamente il controllo elettronico del display o collegarlo manualmente. Se è danneggiato, è possibile sostituire direttamente il controllo elettronico del display o collegarlo manualmente Intatto.
Fase 2: verificare la presenza di saldature virtuali, cortocircuiti, danni o bruciature dei componenti della scheda di controllo principale interna.
Fase 3: se le condizioni lo consentono, posizionare T1 (sensore di temperatura interna) sotto l'acqua fredda (la temperatura dell'acqua deve essere inferiore a 20°C), quindi accendere l'alimentazione e misurare con un misuratore se l'alimentazione di rete viene erogata ai terminali L e N collegati all'alimentazione dell'unità esterna. Se le condizioni lo consentono, posizionare T1 (sensore di temperatura interna) sotto l'acqua fredda (la temperatura dell'acqua deve essere inferiore a 20°C), quindi accendere l'alimentazione e misurare con un misuratore se l'alimentazione di rete è presente ai terminali L e N collegati all'alimentazione dell'unità esterna. Se l'alimentazione di rete non viene erogata, è possibile che sia presente un guasto nel controllo elettrico interno, che deve essere sostituito. Se l'alimentazione di rete è presente, continuare.
Fase 4: Verificare la presenza di saldature virtuali, cortocircuiti o componenti danneggiati nei componenti del circuito della scheda del display
- L'armadio visualizza E9, errore di apertura e chiusura; controllare il controllo elettronico interno, il motore di apertura e chiusura, l'interruttore fotoelettrico e i componenti del telaio di uscita dell'aria. componenti.
Fase 1: Ruotare manualmente lo sportello in posizione semiaperta o semichiusa, quindi utilizzare un multimetro in modalità CA per misurare la seguente tensione.
| sequenza di linee | 1 piede (giallo) | 2 gambe (nere) | 3 gambe (rosse) |
| Funzioni corrispondenti | N linea neutra | Aprire e chiudere la porta | Aprire e chiudere la porta |
| Tensione CA con linea N all'apertura | N linea neutra | 220V | 265V |
| Tensione CA con linea N quando è chiusa | N linea neutra | 265V | 220V |
Osservare se la porta si chiude in questo momento. Se non si chiude, misurare la tensione CA tra il pin 1 (giallo) e il pin 3 (rosso) per verificare la presenza di 220 V (come mostrato nella figura seguente). Se non si verifica alcuna chiusura, misurare la tensione CA tra il pin 1 (giallo) e il pin 3 (rosso) per verificare la presenza di 220 V (come mostrato nella figura seguente). Se l'uscita di rete è a 220 V e non c'è chiusura, il motore è difettoso e va sostituito.

Controllo dell'apertura e della chiusura della porta Feedback dall'interruttore fotoelettrico
Fase 2: se non c'è alcun segnale di azionamento a 220 V in uscita dalla prima fase di misurazione, misurare il feedback dell'interruttore fotoelettrico sulla scheda madre di controllo elettronico e misurare la seguente tensione: (se si dispone di un componente interruttore fotoelettrico già pronto, saltare questa fase) scheda madre di controllo elettronico e misurare la seguente tensione: (se è presente un componente interruttore fotoelettrico già pronto, saltare questo passaggio)
| sequenza di linee | 1 piede | 2 piedi | 3 piedi | 4 piedi |
| rosso | (Bianco) | (Marrone) | (Giallo) | |
| Funzioni corrispondenti | aperto | +5v | motivi | chiudere |
| Livello di tensione all'apertura | +5v | +5v | motivi | 0v |
| Livello di tensione quando è chiuso | 0v | +5v | motivi | +5v |
| Mezzo aperto, mezzo chiuso | 0v | +5v | motivi | 0v |
- Misurare la tensione tra il pin 2 (bianco) e il pin 3 (marrone) della presa di feedback sulla scheda elettronica di controllo per verificare se è presente una tensione di 5 V CC. Se non è presente tale tensione, determinare il guasto del controllo elettronico interno e sostituirlo;; se non è presente tale tensione, determinare il guasto del controllo elettronico interno e sostituirlo. Misurare la tensione tra il pin 2 (bianco) e il pin 3 (marrone) della presa di feedback sulla scheda di controllo elettronico per verificare la presenza di una tensione di 5 V CC.
- Accendere e spegnere la porta per metà, quindi riaccenderla. Verificare se la tensione tra il pin 1 (rosso) e la massa e il pin 4 (giallo) e la massa soddisfa le regole di cui sopra. Controllare se la tensione tra il pin 1 (rosso) e la terra e il pin 4 (giallo) e la terra soddisfa le regole di cui sopra. Se la tensione può essere soddisfatta, si stabilisce che c'è un guasto nel controllo elettrico interno. Se la tensione non può essere soddisfatta, verificare quanto segue.
Controllare se la fotocellula dello sportello dell'interruttore è bloccata da oggetti estranei. Se ci sono oggetti estranei, rimuoverli e provare a riaccendere l'interruttore.
② Controllare se la piastra di blocco della luce della porta dell'interruttore è rotta. Se è rotta, sostituire il componente del telaio dell'aria.
confermato che non vi è alcun problema con la piastra di blocco della luce del telaio dell'aria, si determina che l'interruttore fotoelettrico è difettoso o peggio ancora.
Fase 3: se sono disponibili componenti per interruttori fotoelettrici già pronti e di buona qualità, seguire i passaggi seguenti per la risoluzione dei problemi.
- Accendere e spegnere la porta a metà e collegare il modulo di commutazione fotoelettrica integrato.
- Assicurarsi che il sensore fotoelettrico sul componente dell'interruttore fotoelettrico non sia ostruito da oggetti estranei.
- Riaccendere l'alimentazione, senza accenderla, e osservare se la porta si chiude: se la porta non si chiude, è stato rilevato un malfunzionamento del comando elettrico interno e si sostituisce il comando elettrico interno. Accendere l'alimentazione, non accenderla, osservare se la porta si chiude in questo momento: se la porta non si chiude, si è determinato un malfunzionamento del controllo elettrico interno e si sostituisce il controllo elettrico interno.
- Se la porta si chiude, proseguire con le 2 fasi seguenti.
① Durante il processo di chiusura della porta, se il sensore fotoelettrico sull'interruttore fotoelettrico viene coperto con la mano, la porta si arresterà per la chiusura
② Durante l'apertura della porta, coprire con la mano il sensore fotoelettrico dell'interruttore fotoelettrico.
. Se il funzionamento di cui sopra non regge, determinare l'ostacolo del controllo elettrico interno e sostituire il controllo elettrico interno. Se l'operazione sopra descritta è valida, verificare che il campo di errore sia nell'interruttore fotoelettrico originale. Se l'operazione di cui sopra è valida, determinare che il campo di guasto è nell'interruttore fotoelettrico originale. Se si determina che la piastra di blocco della luce smette di funzionare, significa che l'interruttore fotoelettrico è difettoso e sostituirlo.
- E1: protezione della comunicazione interna ed esterna: controllo della scheda madre interna, della scheda madre esterna e del reattore. E1: protezione della comunicazione interna ed esterna: controllare la scheda madre interna, la scheda madre esterna, la reattanza, il ponte raddrizzatore, il gruppo di fili di collegamento interno ed esterno.
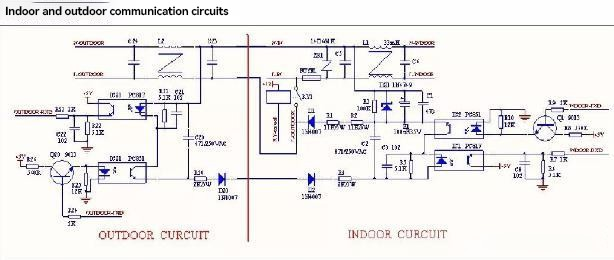
Fase 1: verificare che tutti i collegamenti tra la centralina elettrica e i terminali della linea di alimentazione interna siano collegati correttamente. Una volta confermato, accendere il dispositivo e avviare il raffreddamento/riscaldamento. Misurare la tensione CA tra i terminali L e N per verificare la presenza di un'uscita di rete (Nota: effettuare il test entro 2 minuti dall'accensione e dall'avvio. Se dopo 2 minuti non vi è alcuna uscita di rete, ciò è dovuto alla disconnessione del relè principale dell'alimentazione interna ed esterna) Quando il relè è chiuso, se non vi è alcuna uscita di rete, ciò è dovuto alla disconnessione del relè principale dell'alimentazione interna ed esterna. Quando il relè è chiuso, se non c'è uscita di rete, si determina un guasto nel controllo elettrico interno e il controllo elettrico interno deve essere sostituito. sostituito
Fase 2: dopo aver confermato che l'unità interna dispone di un'uscita di rete, verificare se i collegamenti L, N e S esterni sono corretti, se i fili di collegamento interni ed esterni sono intatti e misurare se i terminali di collegamento esterni L e N dispongono di un ingresso di rete. Dopo aver confermato che l'unità interna ha l'uscita di rete, verificare se i collegamenti L, N e S esterni sono corretti, se i fili di collegamento interni ed esterni sono intatti e misurare se i terminali di collegamento esterni L e N hanno l'ingresso di rete. Se i fili di collegamento interni ed esterni sono intatti e collegati correttamente, e l'unità esterna non riceve tensione in ingresso, è possibile stabilire che l'unità interna e quella esterna sono collegate alla rete elettrica. Se i fili di collegamento interni ed esterni sono intatti e collegati correttamente e l'unità esterna non riceve tensione in ingresso, è possibile determinare che il gruppo di fili di collegamento interni ed esterni è difettoso e sostituirlo.
Fase 3: dopo essersi assicurati che l'unità esterna sia alimentata dalla rete elettrica, osservare se la spia di alimentazione del controllo elettrico esterno è accesa. Se la spia non è accesa, procedere come segue per la risoluzione dei problemi. Se la spia non è accesa, procedere come segue per la risoluzione dei problemi.
- Verificare che i fili di collegamento del controllo elettrico, le reattanze e le induttanze dell'unità esterna siano inseriti correttamente. In caso di problemi di collegamento, provare a collegarli prima di riaccenderli. In caso di problemi di collegamento, provare a collegarli prima di riaccenderli.
- Se si conferma che tutti i cablaggi sono corretti, si stabilisce che c'è un guasto al controllo elettrico esterno e che il controllo elettrico esterno deve essere sostituito. sostituito.
Fase 4: Se la spia dell'unità esterna è accesa, si tratta di un guasto del circuito di comunicazione. Misurare in base ai seguenti passaggi.
- Quando l'intera macchina non è alimentata, utilizzare un multimetro per misurare la resistenza tra N-S (nota)
Per misurare la resistenza di N-S, le sonde positive e negative devono essere misurate in modo incrociato, altrimenti ciò influisce sul giudizio della misura. La resistenza normale è infinita). Se la resistenza non è infinita, per continuare la misurazione è necessario scollegare le linee di collegamento interne ed esterne. Se la resistenza non è infinita, è necessario scollegare le linee di collegamento interne ed esterne per continuare la misurazione. Se la resistenza tra N-S interni non è infinita, si giudica l'ostacolo di controllo elettrico interno. Se la resistenza tra l'interno N-S non è infinita, viene giudicato l'ostacolo di controllo elettrico interno.
- Dopo aver confermato che la resistenza è normale, accendere l'intera macchina e misurare la tensione tra N-S con un multimetro in modalità CC. deve soddisfare contemporaneamente i tre punti seguenti
:
In primo luogo, a causa delle fluttuazioni di tensione irregolari e rapide, è necessario misurare la tensione per più di 2 minuti, osservare attentamente l'intervallo di fluttuazioni di tensione e quindi formulare un giudizio; e poi, le fluttuazioni di tensione saranno misurate dalle fluttuazioni di tensione dell'intervallo di tensione. fluttuazioni di tensione e quindi esprimere un giudizio.
Fase 2: il relè principale dell'alimentatore esterno sul pannello interno deve essere chiuso, cioè l'esterno deve essere alimentato. Lo schema di tensione è il seguente
L'intervallo di tensione normale oscilla tra 3-22V.
② Se l'intervallo di tensione misurato salta tra 3-5,5 V, indica che c'è un problema con la trasmissione interna ed è stato determinato che c'è un guasto nel controllo elettrico interno. Se l'intervallo di tensione misurato salta tra 3-5,5 V, significa che c'è un problema con la trasmissione interna e che è stato determinato un guasto nel controllo elettrico interno.
③ Se la tensione massima misurata è superiore a 25V, indica che il regolatore di tensione da 24 V per interni è guasto e che si è determinato un guasto nel controllo elettrico interno, che deve essere sostituito. Se la tensione massima misurata è superiore a 25V, indica che il regolatore di tensione interno a 24 V è guasto e che è presente un guasto nel controllo elettrico interno, che deve essere sostituito.
④ Se l'intervallo di tensione misurato è 0-2V, indica un malfunzionamento del controllo elettrico interno e richiede la sostituzione.
⑤ Se l'intervallo di tensione misurato salta tra 3-11,5 V, indica che c'è un problema di ricezione esterna e che il controllo elettrico esterno è difettoso e richiede la sostituzione del controllo elettrico esterno. Se l'intervallo di tensione misurato salta tra 15-25 V, indica che c'è un problema di trasmissione esterna e che il controllo elettrico esterno è difettoso e richiede la sostituzione del controllo elettrico esterno. Se l'intervallo di tensione misurato salta tra 15 e 25 V, indica che c'è un problema con la trasmissione esterna e il controllo elettrico esterno è considerato difettoso e richiede la sostituzione del controllo elettrico esterno. Il controllo elettrico esterno è difettoso e richiede la sostituzione del controllo elettrico esterno.
Fase 3: dopo aver confermato che la tensione tra N-S è normale, utilizzare una scheda di test di conversione di frequenza per controllare i valori di temperatura dei sensori interni T1 e T2. Se i valori di temperatura dei sensori T1 e T2 visualizzano -66 gradi, significa che c'è un problema con la ricezione esterna e che il controllo elettrico esterno è difettoso. Se i valori di temperatura dei sensori T1 e T2 visualizzano -66 gradi, significa che c'è un problema di ricezione esterna e che il controllo elettrico esterno è difettoso. Se i valori di temperatura dei sensori T1 e T2 sono normali, significa che c'è un problema di ricezione interna e che il controllo principale interno è difettoso. Sostituire il controllo elettrico interno. Sostituire il comando elettrico interno.
- Display in cabina Eb, display su gancio E3: stallo del ventilatore interno; controllare la scheda madre dell'unità interna, il ventilatore interno e la pala del vento interna.
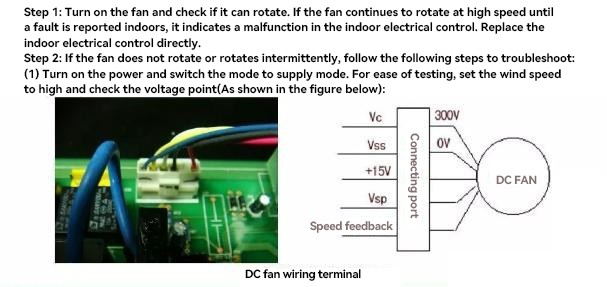
| sequenza di linee | 1 piede (rosso) | Tre gambe (nero) | 4 piedi (bianco) | 5 piedi (giallo) | 6 piedi (blu) |
| Funzione del pin | Alimentazione della ventola | Alimentazione della ventola | Alimentazione del circuito di controllo della ventola | Unità ventilatore | Feedback dei fan |
| Tensione CC corrispondente | +310V | motivi | +15V | 0~5.6V | 0~15V |
Misurare la tensione di lavoro: verificare se la tensione tra il pin 1 (rosso), il pin 4 (bianco) e il pin 3 (nero) corrisponde alla tensione indicata nella tabella precedente. Se non corrisponde alla tensione, indica un guasto nel controllo elettrico interno e deve essere sostituito; (2) dopo aver confermato che l'ingresso dell'alimentazione è normale, misurare la tensione di lavoro. Misurare la tensione di lavoro: verificare se la tensione tra il pin 1 (rosso, il pin 4 (bianco) e il pin 3 (nero) corrisponde alla tensione indicata nella tabella precedente. La tensione di pilotaggio del pin 5 (giallo) per verificare se è normale. Durante il normale funzionamento, la tensione di pilotaggio della ventola è approssimativamente compresa tra 2,7V e 4,6V. La tensione di pilotaggio è una tensione CC relativamente stabile con piccole fluttuazioni di tensione. Se si verifica una delle tre situazioni seguenti.
Non c'è tensione di pilotaggio della ventola nel controllo elettronico o la tensione di pilotaggio è inferiore a 2V; ① Non c'è tensione di pilotaggio della ventola nel controllo elettronico o la tensione di pilotaggio è inferiore a 2V.
La tensione di pilotaggio è superiore a +6V; ② La tensione di pilotaggio è superiore a +6V.
③ La tensione di pilotaggio salta e fluttua in un intervallo superiore a 1V; se l'azionamento del ventilatore è anomalo e il controllo elettrico interno è difettoso, sostituire il controllo elettrico interno: se la tensione di pilotaggio è normale ma il ventilatore continua a non girare o a ruotare a intermittenza, verificare se le pale del ventilatore interno sono normali. controllo elettrico interno: se la tensione di azionamento è normale ma il ventilatore continua a non girare o a ruotare a intermittenza, verificare se le pale del ventilatore interno sono normali. Se non sono normali, sostituire le pale del ventilatore, altrimenti si ritiene che il ventilatore sia difettoso e sostituirlo.
- Il pannello interno visualizza P0: guasto modulo IPM; controllare la scheda di controllo elettrico esterna, il compressore, il gruppo di fili di collegamento del compressore.
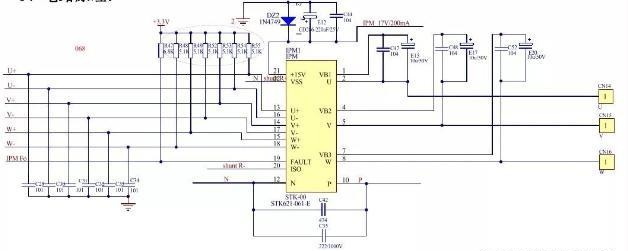
Sanyo STK621-061-E circuito del moduloFase 1: Aprire il coperchio superiore esterno e ispezionare attentamente il modulo di controllo elettronico esterno del compressore (il modulo più vicino al gruppo di linee di collegamento del compressore blu, rosso e nero sulla scheda di controllo elettronico) e le resistenze vicino al modulo per qualsiasi modulo più vicino alla linea di collegamento del compressore gruppo blu, rosso e nero sulla scheda di controllo elettronico) e le resistenze vicino al modulo per verificare che non vi siano bruciature o crepe evidenti. Se si riscontrano bruciature o crepe evidenti, si ritiene che vi sia un guasto al controllo elettronico e che il controllo elettronico esterno debba essere sostituito. Se si riscontrano bruciature o crepe evidenti, si ritiene che vi sia un guasto al controllo elettronico e che il controllo elettronico esterno debba essere sostituito.
Fase 2: verificare se il cablaggio UAV/W sul controllo elettronico e sul compressore è corretto. Dopo aver confermato la correttezza del cablaggio, scollegare il gruppo di fili di collegamento tra il compressore e il controllo elettronico, quindi misurare la resistenza tra l'ingresso U/W del compressore. Dopo aver verificato la correttezza del cablaggio, scollegare il gruppo di fili di collegamento tra il compressore e il controllo elettronico, quindi misurare la resistenza tra l'ingresso U/W del compressore. Il valore corretto della resistenza dovrebbe essere 0,5-2Q. Se il valore della resistenza è significativamente alto, smontare l'unità esterna e verificare se il compressore è in grado di funzionare. Se il valore della resistenza è significativamente alto, smontare l'unità esterna e verificare se il gruppo di fili di collegamento del compressore è inserito correttamente e se è bruciato. Dopo aver confermato che il gruppo di fili di collegamento è a posto, misurare la resistenza tra l'ingresso U e l'ingresso W del compressore. Dopo aver confermato che il gruppo di fili di collegamento è a posto, misurare la resistenza tra U /V/W del compressore. Se la resistenza è superiore a 10Q, stabilire che il compressore è difettoso e sostituirlo.
Fase 3: scollegare il gruppo di fili di collegamento tra il compressore e il modulo (nota: è necessario assicurarsi che il gruppo di fili di collegamento tra il compressore e il controllo elettronico sia scollegato e che gli altri cablaggi rimangano invariati, altrimenti la misurazione è priva di significato). (nota: è necessario assicurarsi che il gruppo di fili di collegamento tra il compressore e il controllo elettronico sia scollegato e che gli altri cablaggi rimangano invariati, altrimenti la misurazione è priva di significato), misurare la seguente resistenza.
- Misurare la resistenza tra U (blu), V (rosso) e W (nero) sulla scheda di controllo elettronico (nota: le sonde positive e negative del multimetro, per un totale di UV, VU, UW, WU, VW, WV, sei combinazioni di resistenze, con un intervallo di resistenza di circa 300KQ-800KQ e una differenza di resistenza inferiore a 10KQ tra le varie combinazioni (ad esempio, la differenza tra le resistenze di U e W). 10KQ tra le combinazioni (ad esempio, la differenza tra la resistenza UV e la resistenza UW): se si verifica una delle due situazioni seguenti, si tratta di una resistenza di tipo VU. Se si verifica una delle due situazioni seguenti, si determina che il guasto del controllo elettrico esterno è stato commutato al controllo elettrico esterno.
Fasi di risoluzione dei problemi: misurare le resistenze UV VU, UW, WU, VW, WV, 6 resistenze combinate, dove la resistenza è inferiore a 100KQ o superiore a 3MQ
La differenza di resistenza tra le combinazioni (ad esempio la differenza di resistenza tra UV e UW) è superiore a 30KQ.
- Misurare U (blu), V (rosso), W (nero) sulla scheda di controllo elettronico e P (polo positivo del condensatore di grande punto, modulo IPM) rispettivamente
La resistenza tra i pin del blocco sarà segnata, e il polo positivo del misuratore sarà collegato a UV/W, e il polo negativo sarà collegato a P. Verranno effettuate tre serie di misurazioni
La differenza di resistenza di linea non è significativa, con una gamma di valori di resistenza compresi tra 200KQ-800KQ e tra combinazioni (ad esempio: UP
Se la differenza di resistenza tra il valore di resistenza di VP e il valore di resistenza di VP è inferiore a 10KQ, si determina che
Guasto al controllo elettrico esterno, sostituire il controllo elettrico esterno.
① La resistenza misurata è inferiore a 50KQ o superiore a 3MQ.
La differenza di resistenza tra le combinazioni (ad esempio, la differenza di resistenza tra UP e VP) è superiore a 30KQ.
- Misurare rispettivamente U (blu), V (rosso), W (nero) sulla scheda di controllo elettronico e N (polo negativo del condensatore a grande punto, modulo IPM)
La resistenza tra i pin del blocco sarà contrassegnata e il polo positivo del multimetro sarà collegato a UAV/W e quello negativo a N. La resistenza tra i pin del blocco sarà contrassegnata e il polo positivo del multimetro sarà collegato a UAV/W e quello negativo a N. Vengono effettuate tre serie di misure
La differenza di resistenza di linea non è significativa, con una gamma di valori di resistenza compresi tra 200KQ-800KQ e tra combinazioni (ad esempio: UN
La differenza di resistenza tra VN e VN è inferiore a 10KQ: se si verifica una delle due situazioni seguenti, determinare
Guasto al controllo elettrico esterno, sostituire il controllo elettrico esterno.
① Quando si misura la resistenza, se è inferiore a 50KQ o superiore a 3MQ.
② La differenza di resistenza tra le combinazioni (ad esempio la differenza di resistenza tra UN e VN) è superiore a 30KQ
- Misurare U+ V+, W+, U-, V-, W-, I valori di resistenza tra i sei azionamenti del compressore e N (U+e N, V+e N, W+e N, U -e N, V -e N, W -e N) sono approssimativamente compresi tra 3KQ-6KQ, e la differenza dei valori di resistenza tra ciascun gruppo misurato deve essere inferiore a 1KQ; se le seguenti situazioni si verificano approssimativamente tra 3KQ-6KQ, e la differenza dei valori di resistenza tra ciascun gruppo misurato dovrebbe essere inferiore a 1KQ; se si verificano le situazioni seguenti Se si verificano le seguenti situazioni, si determina un guasto al controllo elettrico esterno e il controllo elettrico esterno deve essere sostituito: misurare il valore della resistenza tra uno dei sei circuiti di azionamento e il valore della resistenza tra uno dei sei circuiti di azionamento. Il valore della resistenza tra uno dei sei circuiti di azionamento e la massa è significativamente diverso dai valori di resistenza degli altri circuiti (la differenza del valore di resistenza è superiore a 1). differenza di resistenza è superiore a 1KQ), ad esempio: misurare il valore di resistenza tra V+e N, che è superiore a 1KQ e diverso dal valore di resistenza tra W+e N. il valore della resistenza tra W+e N.
| Punto di misura | Alimentazione a 15 V | Linea N |
| Tensione CC tra la linea N | 15V-17V | 0V |
Fase 4: dopo aver confermato che non ci sono problemi con le due misurazioni precedenti, accendere l'alimentazione e misurare le seguenti tensioni: tensione di 15 V CC tra le linee N e N dell'alimentatore 15V-17VOV15V: c'è un'etichetta sul fondo della scheda PCB. tra le linee N e N dell'alimentatore 15V-17VOV15V: c'è un'etichetta sul fondo della scheda PCB. Se non si trova, cercare il diodo regolatore di tensione IN4749 più vicino al modulo di conversione di frequenza (con modulo di conversione di frequenza). Diodo regolatore di tensione IN4749 più vicino al modulo di conversione di frequenza (con un grande dissipatore di calore e collegato al gruppo di linee di collegamento del compressore) sulla scheda elettronica di controllo esterna, misurare la tensione a entrambe le estremità del diodo regolatore di tensione e verificare se corrisponde alla tensione indicata nella tabella precedente. Se la tensione dell'alimentazione a 15 V è inferiore a 12 V o superiore a 18 V, si determina un guasto nel controllo elettronico esterno e il controllo elettronico esterno deve essere sostituito. Se la tensione dell'alimentazione a 15 V è inferiore a 12 V o superiore a 18 V, si determina un guasto nel controllo elettronico esterno e il controllo elettronico esterno deve essere sostituito. Se non si riscontrano problemi con le misurazioni effettuate nelle tre fasi precedenti, consultare il manuale di manutenzione delle prestazioni del convertitore di frequenza per verificare la presenza di un malfunzionamento del compressore.
- Display interno P1: protezione di tensione: controllare il quadro elettrico esterno; oppure il condizionatore d'aria non presenta alcun guasto.
Fase 1: I seguenti fenomeni sono considerati normali: (1) Quando l'unità esterna è spenta e il controllo elettrico esterno si sta scaricando; (2) Rilevare la tensione. Quando la tensione del bus CC esterno è superiore a 389 V o inferiore a 113 V, viene segnalato un guasto.
Quando la tensione del bus CC è inferiore a 389 V e superiore a 113 V, il guasto viene eliminato". (3) Quando la tensione CA è inferiore a 140 V e dura 10 secondi, viene segnalato un guasto; dopo 30 secondi, quando la tensione CA è ≥ 150 V, il guasto viene ripristinato. (3) Quando la tensione CA è inferiore a 140 V e dura 10 secondi, viene segnalato un guasto; dopo 30 secondi, quando la tensione CA è ≥ 150 V, il guasto viene ripristinato.
Motivo del malfunzionamento
| Codice di guasto | informazioni sui guasti | Motivo del malfunzionamento e fasi di risoluzione dei problemi |
| P1 | Protezione di tensione | |
| P10 | Protezione dalla bassa tensione | La tensione del bus CC esterno è inferiore a 113V |
| P11 | Protezione dall'alta tensione | La tensione del bus CC esterno è superiore a 389V |
| P12 | Malfunzionamento del 341MCE | Sostituire il comando elettrico esterno |
Fase 2: fasi di misurazione.
- Collegare la scheda di rilevamento della frequenza variabile, accendere l'alimentazione e spegnere il compressore dopo averlo acceso.
- Misurare la tensione del bus DC (tensione tra P e N/positiva e negativa del condensatore di grande punto) con un metro quadrato e osservare il valore campionato della tensione del bus DC della scheda piccola di rilevamento della frequenza variabile (codice di selezione del valore di campionamento della tensione: "Ir341" per la specifica Misurare la tensione del bus CC (tensione tra P e N/tensione positiva e negativa del condensatore a grande punto) con un metro quadrato e osservare il valore campionato della tensione del bus CC della scheda piccola di rilevamento della frequenza variabile (codice di selezione del valore di campionamento della tensione: "Ir341" per il funzionamento specifico). per il funzionamento specifico, vedere le specifiche funzionali della scheda piccola di rilevamento della frequenza variabile). Confrontare la tensione effettiva con il valore campionato della scheda piccola di rilevamento della frequenza variabile. Se lo scostamento del valore della tensione confrontato è Se la deviazione del valore della tensione confrontata è superiore a 20 V, indica un guasto nel controllo elettrico esterno e deve essere sostituito.
Fase 3: per le macchine che segnalano la protezione dalla tensione P1 all'avvio.
Motivo dell'evento: quando la macchina si guasta, al fine di proteggere l'intera macchina, l'unità interna scollega rapidamente il relè principale di Quando il controllo elettronico esterno si sta scaricando, la scheda di rilevamento della conversione di frequenza visualizza P1 P10:
Nota importante: se l'alimentazione viene interrotta subito dopo l'avvio e la scheda di rilevamento della conversione di frequenza non è in funzione, la scheda di rilevamento della conversione di frequenza non sarà in grado di funzionare.
Seguire queste informazioni di guasto per la risoluzione dei problemi; Il display interno del compressore P2 non è un'informazione di guasto, è necessario prestare attenzione a controllare le informazioni di guasto visualizzate sulla scheda di rilevamento della conversione di frequenza prima di segnalare P1 e P10. Seguire queste informazioni sui guasti per la risoluzione dei problemi; La visualizzazione interna del compressore P2 Display interno del compressore P2: controllare il sensore di temperatura sulla parte superiore del compressore e il cavo di collegamento del compressore.
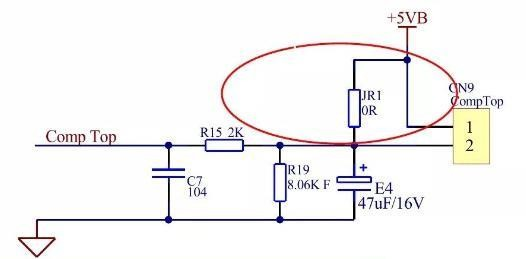
Fase 1: aprire il coperchio superiore esterno, scollegare la spina di protezione della temperatura sulla parte superiore del compressore, collegare un filo alla presa di protezione della temperatura sulla parte superiore del controllo elettrico (scopo: cortocircuitare la presa di protezione della temperatura sulla parte superiore, quindi collegare la presa di rilevamento della frequenza variabile sulla parte superiore). alla presa di protezione della temperatura sulla parte superiore del comando elettrico (scopo: cortocircuitare la presa di protezione della temperatura sulla parte superiore), quindi collegare la scheda di rilevamento della frequenza variabile, accendere l'alimentazione, se la scheda di rilevamento della frequenza variabile getta se la scheda di rilevamento della frequenza variabile lancia la protezione P2, si determina che il comando elettrico esterno è danneggiato; sostituire il comando elettrico esterno. Se la scheda di rilevamento della frequenza variabile lancia la protezione P2, si determina che il controllo elettrico esterno è danneggiato, sostituire il controllo elettrico esterno.
Fase 2: rimuovere il sensore di protezione della temperatura nella parte superiore del compressore e posizionarlo a temperatura ambiente. È necessario assicurarsi che la temperatura del sensore sia vicina alla temperatura ambiente, quindi misurare il valore della resistenza con un metro quadrato. Se il valore della resistenza è infinito o superiore a 1KQ, si determina che il sensore di temperatura superiore è difettoso e lo si sostituisce. superiore a 1KQ, si stabilisce che il sensore di temperatura superiore è difettoso e va sostituito.
Fase 3: quando si rimuove il sensore di protezione della temperatura sulla parte superiore del compressore nella fase 2, prestare attenzione alla temperatura effettiva del compressore. Se la temperatura effettiva del compressore è molto alta, controllare il gruppo di linee di collegamento del compressore per determinare se la sequenza delle linee del compressore è corretta. è corretta.

Fase 4: Se non ci sono problemi con le prime tre fasi e la temperatura del compressore raggiunge una frequenza elevata durante il funzionamento, potrebbe essere causa di un guasto. Consultare il manuale di manutenzione delle prestazioni del convertitore di frequenza per verificare se il compressore o il sistema sono difettosi. Consultare il manuale di manutenzione delle prestazioni del convertitore di frequenza per verificare se il compressore o il sistema sono difettosi.
- La macchina nell'armadio mostra P4 protezione dell'evaporatore interno chiudere il compressore; controllare il controllo elettrico interno, il sensore di temperatura dell'evaporatore, il ventilatore interno, controllare le fasi: refrigerazione: protezione bassa temperatura; riscaldamento: protezione alta temperatura.
Fase 1: verificare che la ventola funzioni normalmente, facendo riferimento a.
- Per determinare se la ventola CA funziona correttamente, fare riferimento alla procedura di risoluzione dei problemi per la ventola CA interna dell'armadio.
- Fare riferimento alle fasi di ricerca guasti per i ventilatori CC interni per determinare se funzionano correttamente Fase 2: fare riferimento alle fasi di ricerca guasti per i guasti E1 per determinare se si tratta di un guasto del sensore o di un guasto della scheda di controllo elettronico corrispondente. Fare riferimento alle fasi di ricerca guasti per i ventilatori CC interni per determinare se funzionano correttamente.
Fase 3: controllare il condotto dell'aria per determinare se l'uscita dell'aria è bloccata, il che influisce sullo scambio termico dell'evaporatore.
Fase 4: consultare il manuale di manutenzione delle prestazioni del convertitore di frequenza per verificare se il sistema è difettoso.
La macchina all'interno dell'armadio mostra P5 protezione condensatore esterno chiudere il compressore; controllare il controllo elettrico interno, il sensore di temperatura del condensatore, il ventilatore esterno, la procedura di risoluzione dei problemi è la stessa di cui sopra;; La macchina all'interno dell'armadio mostra P5 protezione condensatore esterno chiudere il compressore La macchina all'interno dell'armadio mostra P5 protezione condensatore esterno chiudere il compressore; controllare il controllo elettrico interno, il sensore di temperatura del condensatore, la ventola esterna, la procedura di risoluzione dei problemi è la stessa di cui sopra;
- Display della cabina P6, display appeso P4: protezione della posizione del compressore dell'inverter CC; controllare il controllo elettronico esterno, il compressore; è necessario prendere in prestito la scheda di rilevamento della conversione di frequenza per le indagini. Il guasto della scheda di rilevamento della conversione di frequenza è il seguente.
| Codice di guasto | informazioni sui guasti | Passi per la risoluzione dei problemi |
| P4 | Protezione di retroazione per il compressore dell'unità esterna | Consultare l'OP per la risoluzione dei problemi |
| P40 | Errore di comunicazione tra il chip di controllo principale e il chip driver | Sostituire il comando principale esterno |
| P41 | Guasto al circuito di campionamento della corrente del compressore | Sostituire il comando principale esterno |
| P42 | Guasto all'avvio del compressore | Consultare l'OP per la risoluzione dei problemi |
| P43 | Mancanza di protezione di fase | Consultare l'OP per la risoluzione dei problemi |
| P44 | Protezione da velocità zero | Consultare l'OP per la risoluzione dei problemi |
| P45 | Anomalia di sincronizzazione 341PWM | Consultare l'OP per la risoluzione dei problemi |
| P46 | Protezione dallo stallo del compressore | Consultare l'OP per la risoluzione dei problemi |
| P47 | Compressore IPDU bloccato | Non l'ho ancora usato |
| P48 | Regolazione di spegnimento del compressore IPDU | Non l'ho ancora usato |
| P49 | Guasto di sovracorrente del compressore | Consultare l'OP per la risoluzione dei problemi |
- La macchina all'interno dell'armadio mostra che la temperatura di scarico esterna E7 è troppo alta per spegnere il compressore: controllare il controllo elettronico esterno, il sensore della temperatura di scarico, la mancanza di refrigerante; controllare le fasi. La macchina all'interno dell'armadio mostra che la temperatura di scarico esterna E7 è troppo alta per spegnere il compressore.
Il primo passo: scollegare il sensore di temperatura dello scarico, avvicinarne la temperatura a quella ambiente, utilizzare un multimetro per misurare la resistenza del sensore. del sensore, fare riferimento alla risoluzione dei problemi E1, determinare se il guasto del sensore o il guasto della scheda di controllo elettrico corrispondente.
Il secondo passo: consultare il manuale di manutenzione delle prestazioni della macchina di conversione di frequenza per determinare se l'intero sistema è difettoso o se manca il refrigerante. refrigerante.
In quarto luogo, il condizionatore a conversione di frequenza non può visualizzare le fasi e le soluzioni di manutenzione della protezione.
1, Protezione dell'evaporatore interno per la limitazione della frequenza di alta e bassa temperatura
- Fenomeno di guasto: il rilevatore di conversione di frequenza rileva L0 (limite di frequenza dell'evaporatore ad alta e bassa temperatura)
- Portata dei guasti: errore di campionamento della temperatura dell'evaporatore, ostruzione del condotto dell'aria, velocità anomala della ventola
- Fasi di risoluzione dei problemi.
Fase 1: controllare il condotto dell'aria.
- Controllare se il filtro è pieno di polvere. Se l'accumulo di polvere è notevole, è necessario pulirlo.
- Controllare se ci sono detriti nel condotto dell'aria. Non ci devono essere detriti che coprono il condotto dell'aria e che possono compromettere lo scambio di calore.
Fase 2: determinare se la velocità del ventilatore interno è anormalmente bassa
Fase 3: consultare il metodo di risoluzione dei problemi dell'ostacolo E1 e verificare se vi è un errore nel campionamento del sensore di temperatura dell'evaporatore.
Fase 4: consultare il manuale di manutenzione delle prestazioni del convertitore di frequenza per verificare se il sistema è difettoso.
Fase 5: se dopo le operazioni sopra descritte non si confermano problemi, il fenomeno è considerato normale.
2, Protezione di limitazione della frequenza ad alta e bassa temperatura per il condensatore dell'unità esterna
- Fenomeno di guasto: il rilevatore di conversione di frequenza rileva L1 (limite di frequenza del condensatore ad alta temperatura)
- Intervallo nemico: errore di campionamento della temperatura del condensatore, ostruzione del condotto dell'aria, velocità anomala del ventilatore
- Fasi di risoluzione dei problemi.
Fase 1: controllare il condotto dell'aria.
- Controllare se le alette del condensatore sono coperte di polvere. Se la polvere è elevata, è necessario pulirle;
- Controllare se ci sono detriti nel condotto dell'aria. Non ci devono essere detriti che coprono il condotto dell'aria e che possono compromettere lo scambio di calore.
Fase 2: determinare se la velocità del ventilatore esterno è anormalmente bassa
Fase 3: Consultare il metodo di risoluzione dei problemi dell'ostacolo E1 e verificare se vi è un errore nel campionamento del sensore di temperatura del condensatore.
Fase 4: consultare il manuale di manutenzione delle prestazioni del convertitore di frequenza per verificare se il sistema è difettoso.
Fase 5: Se non ci sono problemi confermati dopo le operazioni di cui sopra, il fenomeno è considerato normale.
3, Protezione del limite di frequenza dello scarico del compressore esterno ad alta temperatura
- Fenomeno di guasto: il rilevatore di conversione di frequenza rileva L2 (limite di frequenza dello scarico del compressore ad alta temperatura)
- Campo nemico: errore di campionamento della temperatura di scarico, mancanza di refrigerante
- Fasi di risoluzione dei problemi.
Fasi di risoluzione dei problemi.
Fase 1: determinare se si tratta di un ostacolo del sensore o della scheda di controllo elettronica corrispondente.
Fase 2: consultare il manuale di manutenzione delle prestazioni del convertitore di frequenza per determinare se l'intero sistema è difettoso o se manca il refrigerante.
4, Protezione da sovracorrente con limitazione di frequenza dell'intera macchina
- Fenomeno di guasto: il rilevatore di conversione di frequenza rileva L3 (limite di frequenza attuale)
- Campo di ostacolo nemico: controllo elettrico esterno, pressione del sistema
- Fasi di risoluzione dei problemi.
Fasi di risoluzione dei problemi.
Fase 1: determinare se il campionamento della corrente di controllo elettrica esterna è normale.
Fase 2: verificare se la protezione L0 o L1 viene segnalata contemporaneamente alla protezione L3 per la limitazione della frequenza di corrente e, in caso affermativo, per quale motivo?
Se si verifica, fare riferimento alle fasi di risoluzione dei problemi di L0 o L1 per la risoluzione dei problemi.
Fase 3: verificare se l'intera macchina funziona ad alte frequenze in ambienti di lavoro difficili. In caso affermativo, è da considerarsi normale.
5, Protezione di limitazione della frequenza di tensione dell'intera macchina
- Fenomeno di guasto: il rilevatore di conversione di frequenza rileva L5 (limite di frequenza della tensione)
- Ambito di guasto: controllo elettrico esterno, tensione di ingresso dell'alimentazione
- Fasi di risoluzione dei problemi.
Fasi di risoluzione dei problemi.
Fase 1: Misurare l'ingresso di tensione CA dell'interno per verificare se sta funzionando a bassa tensione. Se la tensione è inferiore a 165V, è considerata una frequenza di tensione normale. Se la tensione è inferiore a 165 V, si considera una frequenza di tensione normale.
Fase 2: misurare se il campionamento della tensione CA è corretto.
Collegare la scheda di rilevamento della conversione di frequenza, accendere l'alimentazione e, dopo aver acceso l'unità esterna, utilizzare un multimetro per misurare gli ingressi L e N dell'unità esterna osservando il valore di campionamento della tensione CA della scheda di rilevamento della conversione di frequenza (codice di selezione del valore di campionamento della tensione: valore di campionamento della tensione). dell'unità esterna osservando il valore di campionamento della tensione CA della scheda di rilevamento della conversione di frequenza (codice di selezione del valore di campionamento della tensione: "AC-Td"), confrontare il valore di campionamento della tensione CA dell'unità esterna con il valore di campionamento della tensione CA della scheda di rilevamento della conversione di frequenza. "AC-Td"), confrontare la tensione effettiva con il valore di campionamento della scheda di rilevamento della frequenza variabile. Se la deviazione di Se la deviazione del valore di tensione confrontato è superiore a 20 V, il controllo elettronico esterno è difettoso e deve essere sostituito.
Fase 2: consultare il pannello di visualizzazione P1 (protezione della tensione) all'interno dell'armadio per verificare e confermare se il campionamento della tensione del bus CC è corretto.
6, protezione di limitazione della frequenza di guasto PFC
- Fenomeno di guasto: il rilevatore di conversione di frequenza rileva L6 (limite di frequenza di guasto PFC)
- Ambito di guasto: Controllo elettrico esterno
- Fasi di risoluzione dei problemi.
Fasi di risoluzione dei problemi.
Controllo elettrico esterno Guasto del modulo PFC, sostituire il controllo elettrico esterno
Cinque, il collegamento con l'aria condizionata centrale degli Stati Uniti.
- L'impostazione del codice dell'indirizzo di debug del condizionatore centrale degli Stati Uniti: Dettagli link: l'indirizzo di debug del condizionatore centrale degli Stati Uniti impostazione del codice
- Codice di guasto per la manutenzione del climatizzatore centrale negli Stati Uniti.
Link ai dettagli: codice di guasto per la manutenzione dell'aria condizionata centrale negli Stati Uniti
- Midea, condizionatore d'aria centralizzato multi-online WIFI, debugging dei guasti del controllore di linea.
Dettagli link: Midea aria condizionata centrale multi-online WIFI filo controller installazione debugging e codice di errore
- Gli Stati Uniti hanno analizzato e risolto i guasti più comuni del condizionatore d'aria centrale.
Link al contenuto dettagliato: Analisi dei guasti comuni e soluzioni dei prodotti finali di climatizzazione Midea END!

 Inglese
Inglese 한국어
한국어 francese
francese Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español italiano
italiano العربية
العربية