Mideaの家庭用エアコンの故障コード、修理手順、中央エアコンの故障コードリンク
First, household air conditioning models before 2019
(A) E, M, H, G series DC inverter hangers:
E0 EEPROM parameter error indication
E1 The communication between the indoor unit and outdoor unit is faulty The E2 zero crossing detection fails
E3 Fan speed out of control
E4 Temperature fuse disconnected protection The E5 outdoor temperature sensor is faulty The E6 indoor temperature sensor is faulty P0 Module Protection
P1 Overvoltage or undervoltage protection P2 Compressor top temperature protection
P4 DC inverter compressor position protection
(2) N, W column DC frequency converter hanging machine:
E0 EEPROM parameter error indication
The E1 communication between the indoor unit and outdoor unit is faulty The E2 zero crossing detection fails
E3 Fan speed out of control
E4 Temperature fuse disconnected protection
The E5 outdoor temperature sensor is faulty or the outdoor 807EEPROM is faulty The E6 indoor temperature sensor is faulty
P0 Module Protection
P1 Overvoltage or undervoltage protection P2 Compressor top temperature protection
P4 DC inverter compressor position protection
(3) C column full DC frequency conversion hanging machine:
E1 EEPROM parameter error indication
E2 The communication between the indoor unit and outdoor unit is faulty E3 Zero crossing error
E4 fan speed out of control
The E5 outdoor temperature sensor is faulty or the outdoor E-square parameter is faulty The E6 indoor temperature sensor is faulty
The E7 outdoor fan speed is out of control
The communication on the E8 display board is faulty
The E9 IPM module is faulty P0 Module Protection
P1 Overvoltage or undervoltage protection P2 Compressor top temperature protection
P3 Protection against low outdoor temperature
P4 DC inverter compressor position protection
(4) I column DC frequency conversion hang-up:
E0 EEPROM parameter error indication
E1 The communication between the indoor unit and outdoor unit is faulty The E2 zero crossing detection fails
E3 Fan speed out of control
E5 The outdoor temperature sensor is faulty or the outdoor E square parameter is faulty The E6 indoor temperature sensor is faulty
The E7 outdoor fan speed is out of control E8 The dust removal is faulty
P0 Module Protection
P1 Overvoltage or undervoltage protection P2 Compressor top temperature protection
P3 Protection against low outdoor temperature
P4 DC inverter compressor position protection
(5) J, K, L, R, K solar series DC inverter hangers
E0 EEPROM parameter error indication
E1 The communication between the indoor unit and outdoor unit is faulty The E2 zero crossing detection fails
E3 Fan speed out of control
E5 The outdoor temperature sensor is faulty or the outdoor E square parameter is faulty The E6 indoor temperature sensor is faulty
The E7 outdoor fan speed is out of control E8 Mode conflict
P0 module protection
P1 Overvoltage or undervoltage protection P2 Compressor top temperature protection
P3 Protection against low outdoor temperature P4 DC inverter compressor position protection
(6) 50FBPY, 50BPY frequency conversion cabinet machine
E01 Module protection four times an hour
Exhaust temperature protection for E03 three times an hour
The P01 indoor panel cannot be protected from the outdoor panel for 2 minutes P02 IPM module protection
P03 High and low voltage protection
P04 Open or short circuit of indoor temperature sensor (room, temperature)
P05 Open or short circuit of outdoor temperature sensor (high or low temperature)
P06 Indoor evaporator temperature protection off compressor (high temperature or low temperature) P07 Outdoor condenser high temperature protection shut off compressor
P09 The outdoor exhaust temperature is too high to shut down the compressor P10 Compressor top temperature protection
P11 Defrosting or cold air protection
The indoor fan of a P12 is overheated
P13 The indoor fan fails to communicate with the switch board for three minutes
(7) Midea series side air outlet embedded air conditioner
Error in reading EEPROM parameter when E0 is powered on
E1 Indoor room temperature T1 sensor is open or short-circuited E2 Indoor evaporator temperature T2 sensor open or short circuit E3 Condenser temperature T3 sensor open or short circuit
Pd quad current protection
(VIII) A, B, FA, FB, FC, GA, GC, H, HA, HB, J, K, N, P, Q1, Q2, Q3, U, V, V1, W, X and other series
split machines
Error reading EEPROM parameter when E1 is powered on Error occurred in the zero crossing detection of E2
E3 Fan speed out of control
E4 Four times current protection
E5 Indoor room temperature sensor open or short circuit
E6 Indoor evaporator temperature sensor is open or short circuit E8 Filter reset failure
(IX) Q Series:
E1 T1 sensor is faulty E2 T2 sensor is faulty E3 T3 sensor is faulty
The E4 T4 sensor is faulty
The E5 network communication is faulty E6 Outdoor protection
The E7 humidifier is faulty
E8 Silent dust removal failure E9 EEPROM error
(10) GA, K series cabinet, J, N, P, Q1, Q2, Q3, R series cabinet, S1, S2, S3, S6, U (U1), V, W, V2 and other series
The E1 T1 sensor is faulty E2 T2 sensor is faulty
E3 T3/T4 sensor is faulty
E4 T4 Sensor failure (Inverter)
E5 network communication failure E6 Outdoor fault
The E7 humidifier is faulty
E8 Electrostatic dust removal is faulty
EQ Automatic door is faulty
Second, home air conditioning 2019 そして beyond:
(1) The indoor unit display board can show その fault 1, cabinet machine fault display:
| protected code | Expressing Content | protected code | Expressing Content |
| PO | PM module malfunction | E0 | EEPROM parameter malfunction |
| P1 | Voltage protection | E1 | T1 sensor malfunction |
| P2 | Compressor top temperature protection | E2 | T2 sensor malfunction |
| P4 | Indoor evaporator protection shutdown compressor (high or low temperature) | E3 | T3/T4、 Exhaust sensor malfunction or outdoor unit E-side parameter malfunction |
| P5 | High temperature protection for outdoor condenser and compressor shutdown | E5 | Communication failure between the main control board and the display button board |
| P6 | Position protection of DC variable frequency compressor | E8 | Indoor and outdoor communication failure |
| P7 | Turn off the compressor when the outdoor exhaust temperature is too high | E9 | Door opening and closing malfunction |
| P8 | Pattern Conflict | Eb | Indoor DC fan stall fault |
| P9 | Anti cold air shut-off fan | L0 | Evaporator high and low temperature frequency limit |
| PA | Grille protection | L1 | Condenser high temperature frequency limit |
| Pd | current protection | L2 | Compressor exhaust high temperature frequency limit |
| L3 | Current frequency limit |
2, hang up fault display:
E0 EEPROM parameter fault
E1 Communication between the indoor unit and outdoor unit is faulty E2 Zero crossing detects the fault
E3 Indoor fan speed out of control
E5 The outdoor temperature sensor is faulty The E6 indoor temperature sensor is faulty E7 Outdoor DC fan stall fault
P0 IPM module protection
P1 Overvoltage or undervoltage protection
P2 Compressor top temperature protection P4 DC inverter compressor position protection
(2) Frequency conversion maintenance small board can display the fault
| protected code | Expressing Content | protected code | Expressing Content |
| P0 | Outdoor unit module protection | E0 | Indoor unit EEPROM parameter failure |
| P1 | Voltage protection | E1 | Indoor and outdoor communication failure |
| P10 | Low voltage protection | E2 | Indoor unit zero crossing detection fault |
| P11 | High voltage protection | E3 | Indoor unit fan stall fault |
| P12 | 341MCE malfunction | E5 | Outdoor unit temperature sensor or E- side fault |
| P2 | Compressor top temperature protection | E50 | Outdoor unit temperature sensor |
| P4 | Feedback protection for outdoor unit compressor | E51 | Outdoor unit E fault |
| P40 | Communication failure between the main control chip and the driver chip | E52 | Outdoor coil T3 temperature sensor malfunction |
| P41 | Compressor current sampling circuit fault | E53 | Outdoor environment T4 temperature sensor malfunction |
| P42 | Compressor startup failure | E54 | Outdoor exhaust temperature sensor malfunction |
| P43 | Compressor phase loss protection | E55 | Outdoor return air temperature sensor malfunction |
| P44 | Compressor zero speed protection | E6 | Indoor peach temperature sensor malfunction |
| protected code | Expressing Content | protected code | Expressing Content |
| P45 | 341PWM synchronization fault | E60 | Indoor unit temperature T1 sensor malfunction |
| P46 | Compressor stall protection | E61 | Indoor unit tube temperature T2 sensor malfunction |
| P47 | IPDU compressor locked | E7 | Outdoor unit DC fan stall fault |
| P48 | IPDU compressor off regulation | Eb | Communication failure between indoor panel and display panel |
| P49 | Compressor overcurrent fault | ||
| P6 | Compressor exhaust high temperature protection | P9 | Evaporator high and low temperature protection |
| P8 | current protection | P90 | Evaporator high temperature protection |
| P80 | Indoor unit current protection | P91 | Evaporator low temperature protection |
| P81 | Outdoor unit current protection | PA | High temperature protection for condenser |
| P82 | Input AC current sampling circuit fault | PF | PFC start laugh stop |
| protected code | Expressing Content |
| L0 | Evaporator high and low temperature frequency limit |
| L1 | Condenser high temperature frequency limit |
| L2 | Compressor exhaust high temperature frequency limit |
| L3 | Current frequency limit |
| L5 | Voltage limited frequency |
| L6 | PFC fault frequency limit |
Three, その United States home frequency conversion air conditioning maintenance steps:
(a) E0 EEPROM parameter failure: check the indoor electric control board, or replace the indoor electric control board;
- If the cabinet displays E1 indoor temperature sensor abnormal, the cabinet displays E2 indoor evaporator temperature sensor abnormal, and the hang-up displays E6 indoor temperature sensor abnormal, check the indoor electric control board and temperature sensor; Troubleshooting steps:
Step 1: Check if the indoor temperature sensor is properly plugged in, and if there is any damage or breakage in the intermediate wire group between the sensor wire group and the motherboard connection Step 2: Replace with a good temperature sensor (if there is no ready-made sensor, skip this step and directly follow step 3). If the fault phenomenon is cancelled, determine the sensor fault and replace the sensor. If the obstacle phenomenon cannot be cancelled, determine the indoor electrical control fault and replace the indoor electrical control:
Step 3: After confirming that the sensor is plugged in properly, unplug the indoor ambient temperature sensor plug to make its temperature close to the ambient temperature. Use a meter to measure the resistance value of the sensor:
Step 4: Roughly estimate the indoor temperature at this time and check the corresponding resistance value
on the thermometer: (Note: When the room temperature is 25 degrees, the sensor resistance value corresponds to 10K. As the temperature increases, the sensor resistance value decreases, and as the temperature decreases, the resistance value increases). If the temperature resistance value deviates greatly (the temperature resistance value deviation is above 5 degrees), the sensor is faulty and the indoor temperature sensor should be replaced.
If the temperature resistance value deviation is very small (the temperature resistance value deviation is below 5 degrees), the electrical control is faulty and the indoor electrical control should be replaced
- Cabinet display E3, hang-up display E5: outdoor temperature sensor failure; Check the outdoor electric control, outdoor temperature sensor, troubleshooting steps;
Step 1: Connect the frequency conversion maintenance tester and observe the fault displayed on the small board
: if E51 is displayed (outdoor unit EEPROM fault) Obstacle: Replace outdoor electrical control:
Step 2: If the frequency conversion maintenance tester displays a sensor fault, lock the range according to the following code:
E52 (outdoor coil T3 temperature sensor fault): reverse check the corresponding resistance value of the thermometer
E53 (outdoor environment T4 temperature sensor fault): reverse check the corresponding resistance value of the thermometer
E54 (outdoor exhaust temperature sensor fault): reverse check the corresponding resistance value of the thermometer)
E55 (outdoor return air temperature sensor fault): reverse check the corresponding resistance value of the thermometer
Step 3: After locking the fault range, you can refer to the troubleshooting steps for E1 faults for troubleshooting:
- Cabinet display E5, motherboard and display key pressing board communication failure, check the indoor motherboard, key pressing board and connector;
Method 1: Bring a normally functioning variable frequency cabinet display board, regardless of the model, and connect it to the indoor electronic control. If the fault disappears, determine the original display electronic control fault and replace it; If the fault does not disappear, it is determined that there is an indoor electrical control fault and the indoor electrical control should be replaced
Method 2: Similarly, bring a normal working frequency conversion cabinet indoor electronic control, regardless of the model, connect the power supply and all loads as well as the display board: if the E5 fault disappears (note: due to possible compatibility issues with the indoor electronic control, as long as the E5 fault is not displayed, it can be judged)
, then determine the original indoor electronic control fault and replace the indoor electronic control: if the E5 fault does not disappear, confirm the display electronic control fault and replace the display electronic control;
Method 3: If there is no condition for displaying electronic control or indoor electronic control, follow the following steps for testing:
Step 1: Observe whether the display connection wire group is damaged. If it is damaged, you can directly replace the display electronic control or manually connect it Intact;
Step 2: Check whether there is any virtual soldering, short circuit, damage or burning of the indoor main control board components:
Step 3: If conditions permit, place T1 (indoor temperature sensor) under cold water (water temperature must be below 20C), then turn on the power, and use a meter to measure whether there is mains power output at the L and N terminals connected to the outdoor unit power supply. If there is no mains power output, it is determined that there is a fault in the indoor electrical control, and the indoor electrical control should be replaced. If there is mains power output, continue:
Step 4: Check for virtual soldering, short circuits, or damaged components in the display board circuit components
- The cabinet display E9, opening and closing fault; Check indoor electronic control, opening and closing motor, photoelectric switch, air outlet frame components;
Step 1: Manually turn the door to the half open or half closed position, then use a multimeter in AC mode to measure the following voltage:
| line sequence | 1 foot (yellow) | 2 legs (black) | 3 legs (red) |
| Corresponding functions | N neutral line | Open and close the door | Open and close the door |
| AC voltage with N line when opened | N neutral line | 220V | 265V |
| AC voltage with N line when closed | N neutral line | 265V | 220V |
Power on again but do not turn it on. Observe if there is any closing action of the door at this time. If there is no closing action, measure the AC voltage between pin 1 (yellow) and pin 3 (red) to see if there is 220V (as shown in the figure below). If there is 220V mains power output and no closing action, it is determined that the motor is faulty and replaced;

Door opening and closing control Feedback from photoelectric switch
Step 2: If there is no 220V drive signal output from the first step of measurement, measure the feedback of the photoelectric switch on the electronic control motherboard and measure the following voltage: (If there is a ready-made photoelectric switch component, skip this step)
| line sequence | 1 foot | 2 feet | 3 feet | 4 feet |
| red | (White) | (Brown) | (Yellow) | |
| Corresponding functions | open | +5v | grounds | close |
| Voltage level when opened | +5v | +5v | grounds | 0v |
| Voltage level when closed | 0v | +5v | grounds | +5v |
| Half open, half closed | 0v | +5v | grounds | 0v |
- Measure the voltage between pin 2 (white) and pin 3 (brown) of the feedback socket on the electronic control board to see if there is a 5V DC voltage. If there is no such voltage, determine the indoor electronic control fault and replace it;
- Turn the door on and off halfway and then power it on again. Check if the voltage between pin 1 (red) and the ground, and pin 4 (yellow) and the ground can meet the above rules. If the voltage can be met, it is determined that there is a fault in the indoor electrical control. If the voltage cannot be met, then check the following:
Check if the photoelectric switch of the switch door is blocked by foreign objects. If there are foreign objects, remove them and try powering it on again
② Check if the switch door light blocking plate is broken. If it is broken, replace the air frame component. If it is
confirmed that there is no problem with the air frame light blocking plate, then it is determined that the photoelectric switch is faulty or even worse;
Step 3: If there are ready-made and good photoelectric switch components, follow the following steps to troubleshoot:
- Turn the door on and off halfway, and connect the built-in photoelectric switch module:
- Ensure that the photoelectric sensor on the photoelectric switch component is not obstructed by any foreign objects
- Turn on the power again, do not turn it on, observe if there is any closing action of the door at this time: if there is no action of the door, it is determined that there is a malfunction in the indoor electrical control, and replace the indoor electrical control:
- If there is a closing action on the door, continue with the following 2 steps:
① During the process of closing the door, if the photoelectric sensor on the photoelectric switch is covered by hand, will the door stop closing
② During the process of opening the door, cover the photoelectric sensor on the photoelectric switch with your hand
. Does the door stop opening? If the above operation does not hold, determine the indoor electrical control obstacle and replace the indoor electrical control. If the above operation holds, determine that the fault range is in the original photoelectric switch. Light blocking plate for the air outlet frame: Remove the air outlet frame and check if the light blocking plate stops. If it is determined that the light blocking plate stops working, then the photoelectric switch is faulty and replace the photoelectric switch
- Cabinet display E8, hanging machine display E1: indoor and outdoor communication protection: check indoor motherboard, outdoor motherboard, reactor, rectifier bridge, indoor and outdoor connection wire group;
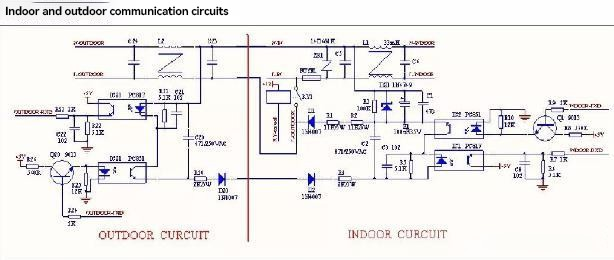
Step 1: Check if all the connections between the electrical control box and the indoor power line terminals are correctly connected. Once confirmed, power on and start cooling/heating. Measure the AC voltage between terminal L and N to see if there is any mains output. (Note: Test within 2 minutes of power on and start up. If there is no mains output after 2 minutes, it will be due to the disconnection of the indoor and outdoor power main relay.) When the relay is closed, if there is no mains output, it is determined that there is a fault in the indoor electrical control and the indoor electrical control should be replaced
Step 2: After confirming that the indoor unit has mains power output, check whether the outdoor L, N, and S connections are correct, whether the indoor and outdoor connection wires are intact, and measure whether the outdoor connection terminals L and N have mains power input. If the indoor and outdoor connection wires are intact and connected correctly, and the outdoor unit has no voltage input, then it is determined that the indoor and outdoor connection wire group is faulty and replaced;
Step 3: After ensuring that the outdoor unit has mains power input, observe whether the outdoor electrical control power indicator light is on. If no indicator light is on, follow the following steps to troubleshoot:
- Check if the outdoor unit's electrical control connection wires, reactors, and inductors are properly plugged in. If there are any issues with the connection, try plugging them in before turning them on again
- If all wiring is confirmed to be correct, it is determined that there is an outdoor electrical control fault and the outdoor electrical control should be replaced:
Step 4: If the outdoor unit indicator light is on, it is a communication circuit fault. Measure according to the following steps:
- When the whole machine is not powered on, use a multimeter to measure the resistance between N-S (note
: to measure the resistance of N-S, the positive and negative probes must be cross measured, otherwise it will affect the judgment of the measurement result). The normal resistance is infinite. If the resistance is not infinite, the indoor and outdoor connection lines need to be disconnected to continue measuring. If the resistance between indoor N-S is not infinite, then the indoor electrical control obstacle is judged. If the resistance between outdoor N-S is not infinite, then the outdoor electrical control obstacle is judged
- After confirming that the resistance is normal, power on the whole machine and measure the voltage between N-S with a multimeter in DC mode. The operation must simultaneously meet the following three points
:
Firstly, due to the irregular and rapid voltage fluctuations, it is required to measure the voltage for more than 2 minutes, carefully observe the range of voltage fluctuations, and then make a judgment;
Step 2: The main relay of the outdoor power supply on the inner panel must be closed, that is, the outdoor must be powered on. The voltage pattern is as follows
The normal voltage range is fluctuating between 3-22V:
② If the measured voltage range jumps between 3-5.5V, it indicates that there is a problem with the indoor transmission, and it is determined that there is a fault in the indoor electrical control. The indoor electrical control needs to be replaced:
③ If the maximum measured voltage is greater than 25V, it indicates that the indoor 24V voltage regulator has failed, and it is determined that there is a fault in the indoor electrical control, which needs to be replaced;
④ If the measured voltage range is 0-2V, it indicates a malfunction in the indoor electrical control and requires replacement
⑤ If the measured voltage range jumps between 3-11.5V, it indicates that there is a problem with the outdoor reception, and the outdoor electrical control is determined to be faulty, requiring replacement of the outdoor electrical control. If the measured voltage range jumps between 15-25V, it indicates that there is a problem with the outdoor transmission, and the outdoor electrical control is determined to be faulty, requiring replacement of the outdoor electrical control
Step 3: After confirming that the voltage between N-S is normal, use a frequency conversion test board to check the temperature values of the indoor T1 and T2 sensors. If the temperature values of the T1 and T2 sensors display -66 degrees, it indicates that there is a problem with the outdoor reception, and the outdoor electrical control is determined to be faulty. Replace the outdoor electrical control. If the temperature values of the T1 and T2 sensors display normally, it indicates that there is a problem with the indoor reception, and the indoor main control is determined to be faulty. Replace the indoor electrical control:
- In-cabinet display Eb, on-hook display E3: indoor fan stall; Check the indoor unit motherboard, inner fan, and inner wind blade;
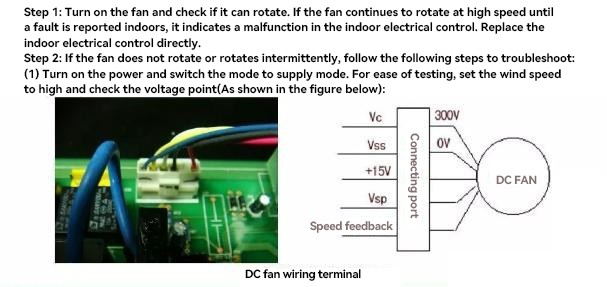
| line sequence | 1 foot (red) | Three legs (black) | 4 feet (white) | 5 feet (yellow) | 6 feet (blue) |
| Pin function | Fan power supply | Fan power supply | Fan control circuit power supply | Fan drive | Fan feedback |
| Corresponding DC voltage | +310V | grounds | +15V | 0~5.6V | 0~15V |
Measure the working voltage: Check if the voltage between pin 1 (red), pin 4 (white) and pin 3 (black) meets the voltage in the table above. If it does not meet the voltage, it indicates a fault in the indoor electrical control and needs to be replaced;(2) After confirming that the power input is normal, measure the driving voltage of pin 5 (yellow) to see if it is normal. During normal operation, the driving voltage of the fan is approximately between 2.7V and 4.6V. The driving voltage is a relatively stable DC voltage with small voltage fluctuations. If one of the following three situations occurs:
① There is no fan driving voltage in the electronic control or the driving voltage is less than 2V;
② The driving voltage is gr eater than+6V;
③ Driving voltage jumps and fluctuates within a range greater than 1V; If the fan drive is abnormal and the indoor electrical control is faulty, replace the indoor electrical control: if the drive voltage is normal but the fan still does not turn or intermittently rotates, check whether the fan blades of the indoor fan are normal. If they are not normal, replace the fan blades. Otherwise, it is judged that the fan is faulty and replaced;
- The indoor panel displays P0: IPM module fault; Check the external electric control board, compressor, compressor connection wire group;
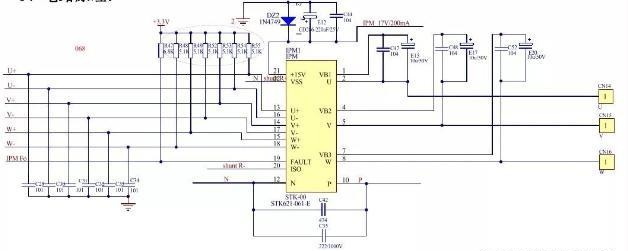
Sanyo STK621-061-E module circuitStep 1: Open the outdoor top cover and carefully inspect the outdoor electronic control compressor drive module (the module closest to the compressor connection line group blue, red, and black on the electronic control board) and the resistors near the module for any signs of explosion or blackening. If obvious burning or cracking is found, it is determined that there is an electronic control fault and the outdoor electronic control should be replaced
Step 2: Check if the UAV/W wiring on the electronic control and compressor is correct. After confirming that the wiring is correct, disconnect the connecting wire group between the compressor and the electronic control, and then measure the resistance between the U input/W of the compressor. The correct resistance value should be 0.5-2Q. If the resistance value is significantly high, disassemble the outdoor unit and test whether the compressor connection wire group is properly plugged in and burned out. After confirming that the connection wire group is fine, measure the resistance between the U/V/W of the compressor. If the resistance is greater than 10Q, determine that the compressor is faulty and replace it
Step 3: Disconnect the connecting wire group between the compressor and the module (note: it is necessary to ensure that the connecting wire group between the compressor and the electronic control is disconnected, and other wiring remains unchanged, otherwise the measurement is meaningless), measure the following resistance:
- Measure the resistance between U (blue), V (red), and W (black) on the electronic control board (note: multimeter positive and negative probes, a total of: UV、VU、UW、WU、VW、WV, Six combinations of resistors, with a resistance range of approximately 300KQ-800KQ, and a resistance difference of less than 10KQ between combinations (such as the difference between UV resistance and UW resistance): If one of the following two situations occurs, it is determined that the outdoor electrical control fault has been switched to the external electrical control
Troubleshooting steps: Measure UV VU、UW、WU、VW、WV, 6 combination resistors, where the resistance is less than 100KQ or greater than3MQ
② The difference in resistance between combinations (e.g. the difference in resistance between UV and UW) is greater than 30KQ:
- Measure U (blue), V (red), W (black) on the electronic control board and P (positive pole of the large point capacitor, IPM module) respectively
The resistance between the block pins will be marked, and the positive pole of the meter will be connected to UV/W, and the negative pole will be connected to P. Three sets of measurements will be taken
The difference in line resistance is not significant, with a range of resistance values between 200KQ-800KQ, and between combinations (for example: UP
If the difference in resistance between the resistance value of VP and the resistance value of VP is less than 10KQ, then it is determined that
Outdoor electrical control failure, replace outdoor electrical control:
① The measured resistance is less than 50KQ or greater than 3MQ;
② The difference in resistance between combinations (e.g. the difference in resistance between UP and VP) is greater than 30KQ:
- Measure U (blue), V (red), W (black) on the electronic control board and N (negative pole of the large point capacitor, IPM module) respectively
The resistance between the block pins will be marked, and the positive pole of the multimeter is connected to UAV/W and the negative pole is connected to N. Three sets of measurements are taken
The difference in line resistance is not significant, with a range of resistance values between 200KQ-800KQ, and between combinations (for example: UN
The difference in resistance between VN and VN is less than 10KQ: If one of the following two situations occurs, then determine
Outdoor electrical control failure, replace outdoor electrical control:
① When measuring resistance, if it is less than 50KQ or greater than 3MQ:
② The difference in resistance between combinations (e.g. the difference in resistance between UN and VN) is greater than 30KQ
- Measure U+ V+、W+、U-、V-、W-, The resistance values between the six compressor drives and N (U+and N, V+ and N, W+and N, U - and N, V - and N, W - and N) are approximately between 3KQ-6KQ, and the difference in resistance values between each measured group should be less than 1KQ; If the following situations occur, it is determined that there is an outdoor electrical control fault and the outdoor electrical control should be replaced: measure the resistance value between one of the six drive circuits and the ground, which is significantly different from the resistance values of the other circuits (the difference in resistance value is greater than 1KQ), for example: measure the resistance value between V+and N, which is greater than 1KQ different from the resistance value between W+and N;
| Measurement point | 15V power supply | N-line |
| DC voltage between N line | 15V-17V | 0V |
Step 4: After confirming that there are no issues with the above two measurements, turn on the power and measure the following voltage: 15V DC voltage between the N and N lines of the power supply 15V-17VOV15V power supply: There is a label on the bottom of the PCB board. If it cannot be found, search for the IN4749 voltage regulator diode closest to the frequency conversion module (with a large heat sink and connected to the compressor connection line group) on the outdoor electronic control board, measure the voltage at both ends of the voltage regulator diode, and see if it meets the voltage in the table above. If the voltage of the 15V power supply is less than 12V or greater than 18V, it is determined that there is a fault in the outdoor electronic control and the outdoor electronic control should be replaced;Step 5: If there are no issues with the measurements taken in the above three steps, refer to the frequency converter performance maintenance manual to confirm if there is a compressor malfunction.
- Indoor display P1: voltage protection: check the outdoor electric control board; Or air conditioning no fault;
Step 1: The following phenomena are considered normal: (1) When the outdoor unit is powered off and the outdoor electrical control is discharging;(2) Detect voltage. When the outdoor DC bus voltage is higher than 389V or lower than 113V, a fault is reported; After 30 seconds
, when the DC bus voltage is lower than 389V and higher than 113V, the fault is eliminated. " (3) When the AC voltage is less than 140V and lasts for 10 seconds, a fault is reported; After 30 seconds, when the AC voltage is ≥ 150V, the fault is restored.
Reason for malfunction
| Fault code | fault information | Reason for malfunction and troubleshooting steps |
| P1 | Voltage protection | |
| P10 | Low voltage protection | The outdoor DC bus voltage is lower than 113V |
| P11 | High voltage protection | The outdoor DC bus voltage is higher than 389V |
| P12 | 341MCE malfunction | Replace outdoor electrical control |
Step 2: Measurement steps:
- Connect the variable frequency detection board, turn on the power, and turn off the compressor after it is turned on:
- Measure the DC bus voltage (voltage between P and N/positive and negative voltage of the large point capacitor) with a square meter, and observe the sampled value of the DC bus voltage of the variable frequency detection small board (voltage sampling value selection code: "Ir341" for specific operation, see the functional specification of the variable frequency detection small board). Compare the actual voltage with the sampled value of the variable frequency detection small board. If the deviation of the compared voltage value is greater than 20V, it indicates a fault in the outdoor electrical control and needs to be replaced
Step 3: For machines that report P1 voltage protection upon startup:
Reason for occurrence: When the machine malfunctions, in order to protect the entire machine, the indoor unit will quickly disconnect the main relay of the outdoor power supply. When the outdoor electronic control is discharging, the frequency conversion detection board will display P1 P10:
Important note: If the power is cut off immediately after starting up and the frequency conversion detection board
reports a P1 fault, it is necessary to pay attention to checking the fault information displayed on the frequency conversion detection board before reporting P1 and P10, which is the true fault information. Please follow this fault information for troubleshooting;The indoor display of P2 compressor top temperature protection: check the temperature sensor at the top of the compressor and the compressor connection cable;
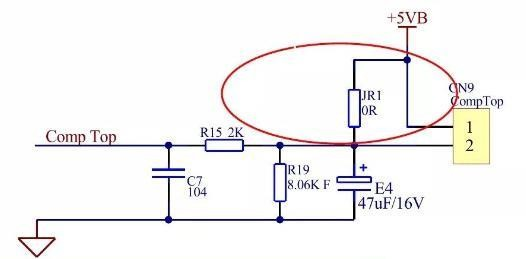
Step 1: Open the outdoor top cover, unplug the temperature protection plug on the top of the compressor, tie a wire to the temperature protection socket on the top of the electric control (purpose: to short-circuit the temperature protection socket on the top), then connect the variable frequency detection board, turn on the power, if the variable frequency detection board throws P2 protection, it is determined that the outdoor electric control is damaged, replace the outdoor electric control:
Step 2: Remove the temperature protection sensor at the top of the compressor and place it at room temperature. It is necessary to ensure that the temperature of the sensor is close to room temperature, and then measure its resistance value with a square meter. If the resistance value is infinite or greater than 1KQ, it is determined that the top temperature sensor is faulty and replaced
Step 3: When removing the temperature protection sensor at the top of the compressor in Step 2, pay attention to the actual temperature of the compressor. If the actual temperature of the compressor is indeed very high, check the compressor connection line group to determine if the compressor line sequence is correct:

Step 4: If there are no problems with the first three steps, and the temperature of the compressor reaches a high frequency during operation, it may cause compressor failure or system malfunction. Refer to the frequency converter performance maintenance manual to confirm whether the compressor or system is faulty:
- The machine in the cabinet shows P4 indoor evaporator protection close compressor; Check the indoor electric control, evaporator temperature sensor, indoor fan, check steps: refrigeration: low temperature protection; Heating: high temperature protection;
Step 1: Check if the fan is operating normally. You can refer to:
- Refer to the troubleshooting steps for the indoor AC fan in the cabinet to determine if the AC fan is functioning properly
- Refer to the troubleshooting steps for indoor DC fans to determine if they are functioning properly Step 2: Refer to the troubleshooting steps for E1 faults to determine whether it is a sensor fault or a corresponding electronic control board fault:
Step 3: Check the air duct to determine if the air outlet is blocked, which affects the heat exchange of the evaporator
Step 4: Refer to the frequency converter performance maintenance manual to confirm if the system is faulty:
The machine inside the cabinet shows P5 outdoor condenser protection close compressor; Check the indoor electric control, condenser temperature sensor, outdoor fan, the troubleshooting procedure is the same as above;
- Cabinet display P6, hanging display P4: DC inverter compressor position protection; Check outdoor electronic control, compressor; Need to borrow frequency conversion detection small board for investigation; The failure of the frequency conversion detection small board is as follows:
| Fault code | fault information | Troubleshooting steps |
| P4 | Feedback protection for outdoor unit compressor | Refer to PO for troubleshooting |
| P40 | Communication failure between the main control chip and the driver chip | Replace the outdoor main control |
| P41 | Compressor current sampling circuit fault | Replace the outdoor main control |
| P42 | Compressor startup failure | Refer to PO for troubleshooting |
| P43 | Lack of phase protection | Refer to PO for troubleshooting |
| P44 | Zero speed protection | Refer to PO for troubleshooting |
| P45 | 341PWM synchronization fault | Refer to PO for troubleshooting |
| P46 | Compressor stall protection | Refer to PO for troubleshooting |
| P47 | IPDU compressor locked | I haven't used it yet |
| P48 | IPDU compressor off regulation | I haven't used it yet |
| P49 | Compressor overcurrent fault | Refer to PO for troubleshooting |
- The machine inside the cabinet shows that the E7 outdoor exhaust temperature is too high to turn off the compressor: check the outdoor electronic control, exhaust temperature sensor, lack of refrigerant; Check steps:
The first step: unplug the exhaust temperature sensor, make its temperature close to the ambient temperature, use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the sensor, refer to E1 troubleshooting, determine whether the sensor fault or the corresponding electrical control board fault;
The second step: refer to the frequency conversion machine performance maintenance manual to determine whether the whole system is faulty or lack of refrigerant;
Fourth, frequency conversion air conditioning can not display protection maintenance steps and solutions:
1、 Indoor evaporator high and low temperature frequency limiting protection
- Fault phenomenon: The frequency conversion detector detects L0 (evaporator high and low temperature frequency limit)
- Fault scope: evaporator temperature sampling error, air duct obstruction, abnormal fan speed
- Troubleshooting steps:
Step 1: Check the air duct:
- Check if the filter screen is filled with dust. If the dust accumulation is severe, it needs to be cleaned
- Check whether there are any debris in the air duct. There should be no debris covering the air duct, which may affect heat exchange
Step 2: Determine if the indoor fan speed is abnormally slow
Step 3: Refer to the E1 obstacle troubleshooting method and check if there is any error in the sampling of the evaporator temperature sensor:
Step 4: Refer to the frequency converter performance maintenance manual to confirm if the system is faulty:
Step 5: If there are no problems confirmed after the above operations, it is considered a normal phenomenon:
2、 High and low temperature frequency limiting protection for outdoor unit condenser
- Fault phenomenon: The frequency conversion detector detects L1 (condenser high temperature frequency limit)
- Enemy range: condenser temperature sampling error, air duct obstruction, abnormal fan speed
- Troubleshooting steps:
Step 1: Check the air duct:
- Check if the condenser fins are covered in dust. If the dust is severe, it needs to be cleaned;
- Check whether there are any debris in the air duct. There should be no debris covering the air duct, which may affect heat exchange
Step 2: Determine if the outdoor fan speed is abnormally slow
Step 3: Refer to the E1 obstacle troubleshooting method and check if there is any error in the sampling of the condenser temperature sensor
Step 4: Refer to the frequency converter performance maintenance manual to confirm if the system is faulty:
Step 5: If there are no problems confirmed after the above operations, it is considered a normal phenomenon
3、 Outdoor compressor exhaust high temperature frequency limit protection
- Fault phenomenon: The frequency conversion detector detects L2 (compressor exhaust high temperature frequency limit)
- Enemy range: Exhaust temperature sampling error, lack of refrigerant
- Troubleshooting steps:
Troubleshooting steps:
Step 1: Determine whether it is a sensor obstacle or the corresponding electronic control board obstacle;
Step 2: Refer to the frequency converter performance maintenance manual to determine if the entire system is faulty or lacking refrigerant
4、 Whole machine overcurrent frequency limiting protection
- Fault phenomenon: The frequency conversion detector detects L3 (current frequency limit)
- Enemy obstacle range: outdoor electrical control, system pressure
- Troubleshooting steps:
Troubleshooting steps:
Step 1: Determine if the outdoor electrical control current sampling is normal:
Step 2: Pay attention to whether L0 or L1 protection is also reported at the same time as L3 current frequency limiting protection,
If it occurs, refer to the troubleshooting steps of L0 or L1 for troubleshooting;
Step 3: Check if the entire machine is operating at high frequencies in harsh working environments. If so, it is considered normal
5、 Whole machine voltage frequency limiting protection
- Fault phenomenon: The frequency conversion detector detects L5 (voltage frequency limit)
- Fault scope: Outdoor electrical control, power input voltage
- Troubleshooting steps:
Troubleshooting steps:
Step 1: Measure the indoor AC voltage input to see if it is operating at low voltage. If the voltage is below 165V, it is considered a normal voltage frequency limiting situation
Step 2: Measure whether the AC voltage sampling is correct:
Connect the frequency conversion detection board, turn on the power, and after the outdoor unit is powered on, use a multimeter to measure the L and N inputs of the outdoor unit while observing the AC voltage sampling value of the frequency conversion detection board (voltage sampling value selection code: “AC-Td”), Compare the actual voltage with the sampled value of the variable frequency detection board. If the deviation of the compared voltage value is greater than 20V, the outdoor electronic control is faulty and needs to be replaced
Step 2: Refer to the display panel P1 (voltage protection) inside the cabinet to check and confirm whether the DC bus voltage sampling is correct;
6、 PFC fault frequency limiting protection
- Fault phenomenon: The frequency conversion detector detects L6 (PFC fault frequency limit)
- Fault scope: Outdoor electrical control
- Troubleshooting steps:
Troubleshooting steps:
Outdoor electric control PFC module failure, replace outdoor electric control
Five, the United States central air conditioning link:
- The United States central air conditioning debugging address code setting: Details link: the United States central air conditioning debugging address code setting
- The United States central air conditioning maintenance fault code:
Details link: the United States central air conditioning maintenance fault code
- Midea central air conditioning multi-online WIFI line controller fault debugging:
Details link: Midea central air conditioning multi-online WIFI wire controller installation debugging and fault code
- the United States central air conditioning end common fault analysis and solutions;
Detailed content link: Midea central air conditioning end products common fault analysis and solutions END!

 英語
英語 한국어
한국어 フランセ
フランセ ドイツ語
ドイツ語 スペイン語
スペイン語 イタリア語
イタリア語 العربية
العربية
.jpg)